Best practices in the implementation of predictive maintenance - a field report
Predictive maintenance: What intelligent maintenance strategies and best practices are there? We'll show you. For a long time, the industry has focused on the manufacture and sale of products and systems and neglected the aftersales market. The networking of machines and the collection of real-time data offers the opportunity to view data in new contexts. This is associated with various benefits for the company, such as optimization of production quality, sustainable machine operation and the implementation of predictive maintenance. For the operator, this ideally means less machine downtime and increased productivity.
The "intelligent" wind turbine
 Together with our customer ZF, a leading technology group in driveline and chassis technology, we have developed the topic of Predictive maintenance in the area Wind energy and would like to share our findings, experiences and various practical challenges with you.
Together with our customer ZF, a leading technology group in driveline and chassis technology, we have developed the topic of Predictive maintenance in the area Wind energy and would like to share our findings, experiences and various practical challenges with you.
ZF manufactures gearboxes for wind turbines, which are very difficult to maintain - for example, because they are located in the middle of the sea. The aim now is to develop the "intelligent" wind turbine in order to minimize downtimes and enable efficient maintenance.
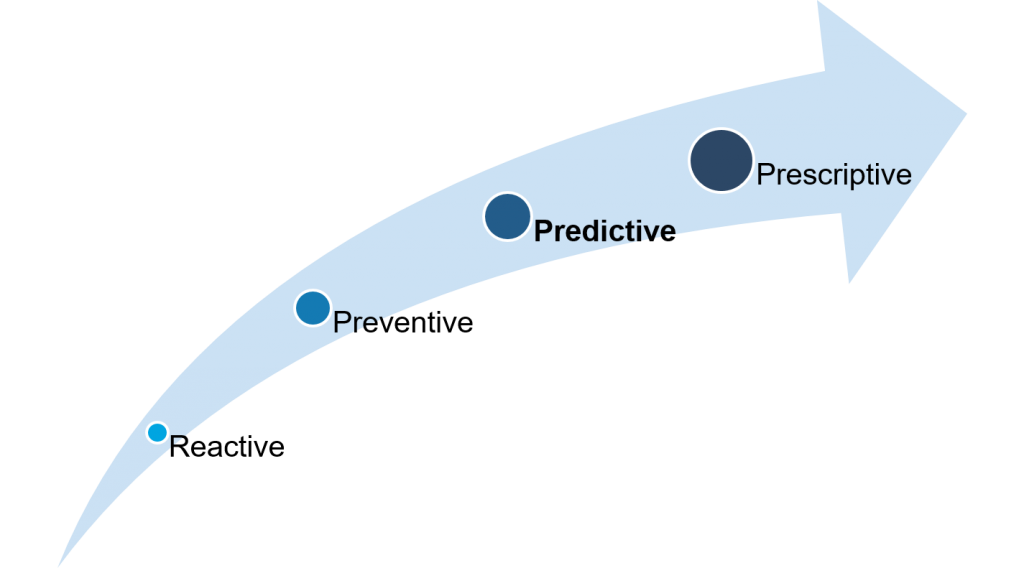
Maintenance strategies
In the area of intelligent machine maintenance, a distinction can be made between the following maintenance strategies:
- Reactive maintenance: The gearbox of the wind turbine is only serviced in the event of an acute failure.
- Preventive maintenance: Predefined maintenance intervals prevent failure depending on usage, i.e. for example wind turbines in zones with strong winds (ocean) are maintained monthly, but only annually in zones with weaker winds (desert).
- Predictive maintenance: machines are maintained according to their condition. The condition data on a wind turbine can be used to predict when the gearbox needs to be replaced, for example.
- Prescriptive maintenance: Automatic action decisions are made, such as independently ordering a spare part for a wind turbine.
Best practices in the predictive maintenance project
Our predictive maintenance project experience has proven the following recommendations for action:
- Solid data management: The flood of data must be made manageable, i.e. you should always have as accurate a picture as possible of what data needs to be collected or for what periods of time the data is stored. Real data from the field is essential for this.
- Versioning and traceability: Complete and traceable documentation allows analyses to be reproduced or any errors in the algorithm to be corrected.
- Modularity: In order to change or renew components of the software without affecting other areas, they should be encapsulated from one another.
- Data integrity: It must be ensured that the data is the same in the value range at all levels, especially in the data memory and in processing algorithms. The same rules for e.g. rounding or the number of decimal places must be guaranteed everywhere. This prevents errors.
- Data exploration: The aim is to find new features and correlations in the data as well as suitable modeling techniques. The data platform should have advantages for the expert who develops with it.
Conclusion
Robust data collection and a modular structure of the software system are crucial for a high-quality predictive maintenance application.
The Internet of Things and, above all, the cloud serve as door openers for AI applications in traditional industry. However, the topic also poses particular challenges in this environment when engineers and software "meet". It is essential that real data is the key to a successful project. We are well on the way to the "maintenance strategy of the future" - self-maintaining machines.
Co-author Timo Demler
More about Condition-Based Maintenance for ropeways with ZF ProVID
Find out more about predictive maintenance here
How does predictive maintenance differ from other maintenance methods?